Experiment 8: Determination of Clotting Time by Capillary Glass Tube Method
AIM
To determine the clotting time of my own blood sample by capillary glass tube method.Requirements
- Lancet- Denatured spirit or ethanol solution
- Cotton swab
- Filter paper
- Stopwatch
- Capillary tube
References
Practical handbook of Human Anatomy and Physiology by S R Kale. Nirali Prakashan, Eighth Edition, 2002, Page number 32 to 33Introduction
A clotting time practical is a procedure that measures how long it takes for blood to clot. It is used to screen for bleeding disorders and monitor conditions like anticoagulant therapy. The principle of clotting time, also known as coagulation time, is based on the process of hemostasis, which is the body's mechanism to stop bleeding. This process involves a complex series of reactions that ultimately lead to the formation of a blood clot.

Key Components
- Blood coagulation cascade: This is a series of enzymatic reactions involving various clotting factors in the blood. These factors are activated in a specific sequence, leading to the formation of a stable fibrin clot.
- Fibrinogen to fibrin: The final step in the coagulation cascade is the conversion of fibrinogen, a soluble protein, into fibrin, an insoluble protein. Fibrin molecules then cross-link to form a mesh-like network that traps blood cells and platelets, forming the clot.
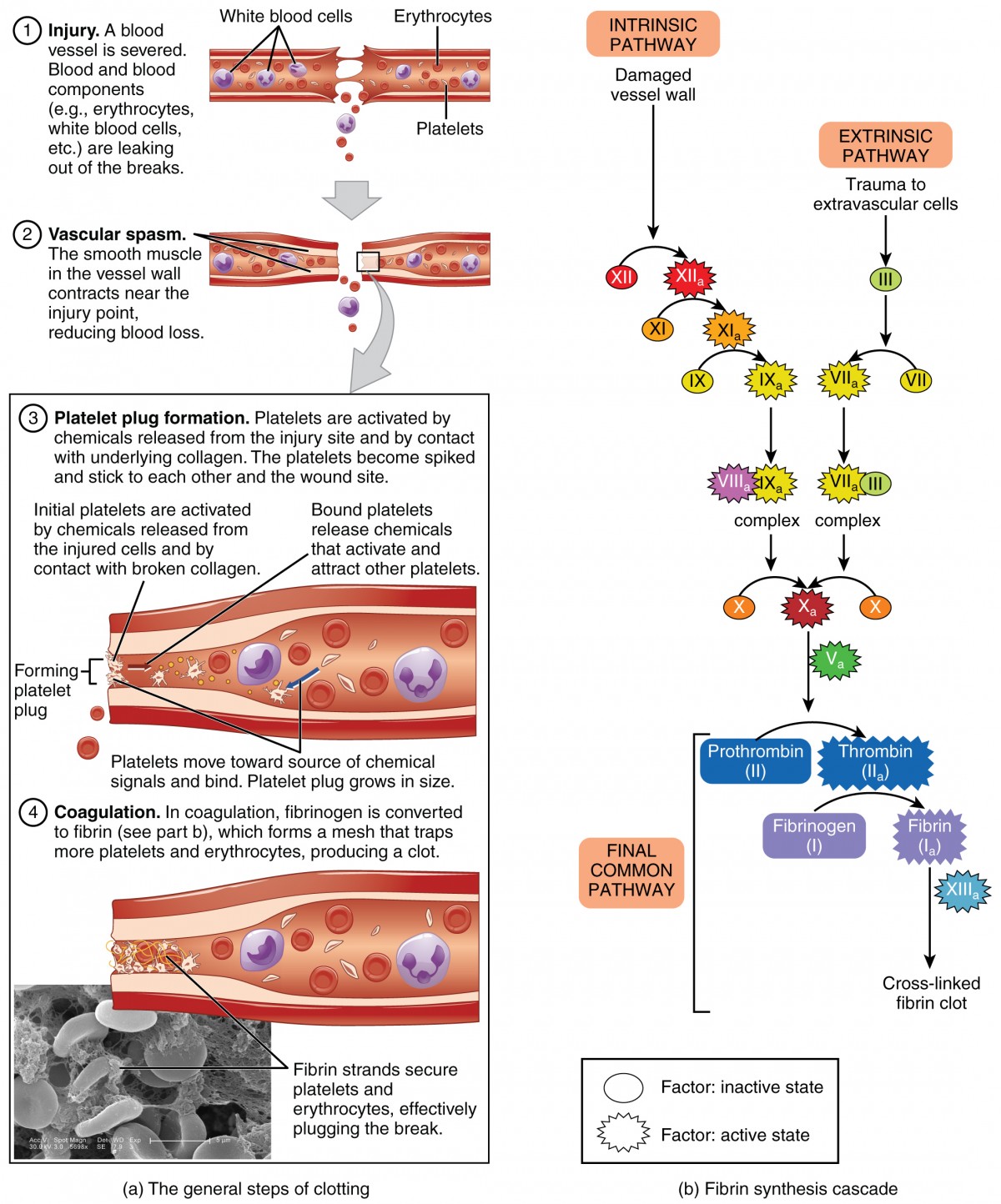
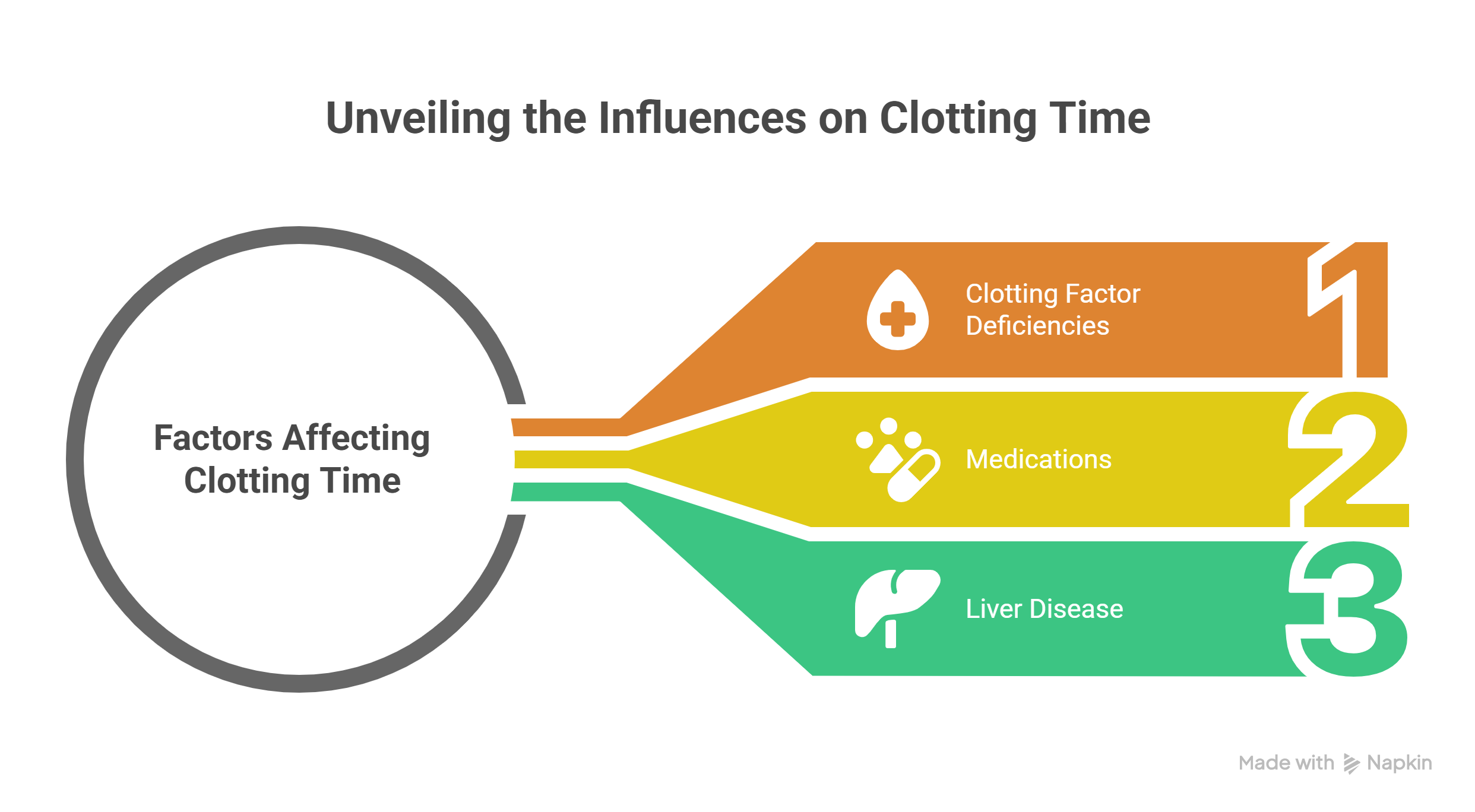
Factors Affecting Clotting Time
- Clotting factor deficiencies: A deficiency in one or more clotting factors can impair the coagulation cascade and prolong clotting time.
- Medications: Anticoagulants or blood thinners can interfere with the coagulation process and increase clotting time.
- Liver disease: The liver produces many clotting factors. Liver damage can reduce their production and prolong clotting time.
Procedure using Capillary Glass Tube Method
- Sterilize the fingertip and make a bold prick with a sterilized needle to allow free flow of blood.
- Collect the blood into a capillary glass tube about 15 centimeters long.
- Keep the tube undisturbed in a horizontal position for one to two minutes.
- Break off a small bit of the tube every 30 seconds until a fine thread of clotted blood appears.
- Stop the stopwatch when the thread appears.
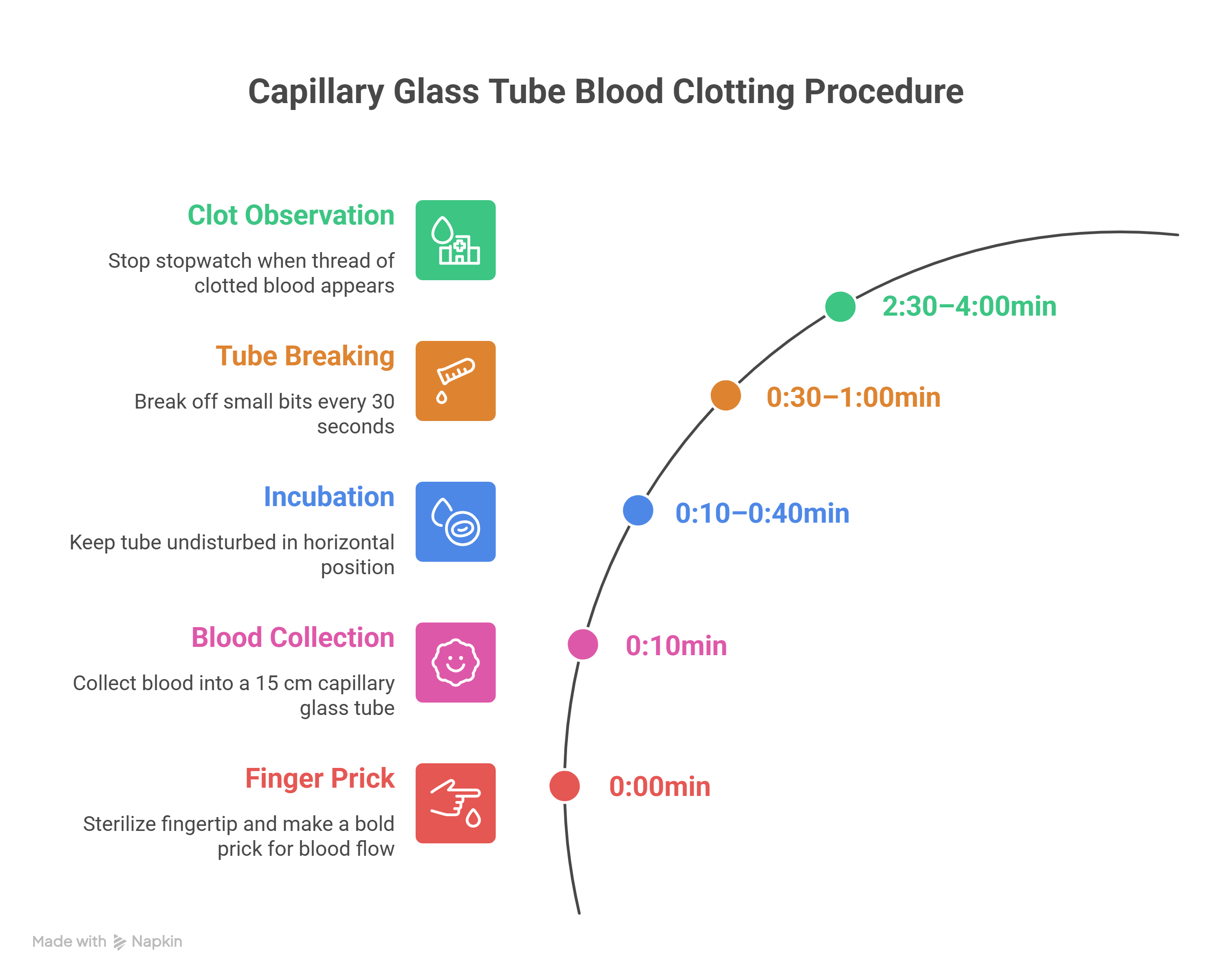
This duration from the appearance of blood to the formation of a clot is recorded as the clotting time.