Experiment 4: Microscopic Study of Epithelial and Connective Tissue
AIM
Microscopic study of epithelial and connective tissue.Requirements
- Permanent slides- Compound microscope
References
Inderbir S. Textbook of Human Histology with Colour Atlas. 6th ed. New Delhi: Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers; 2011Introduction
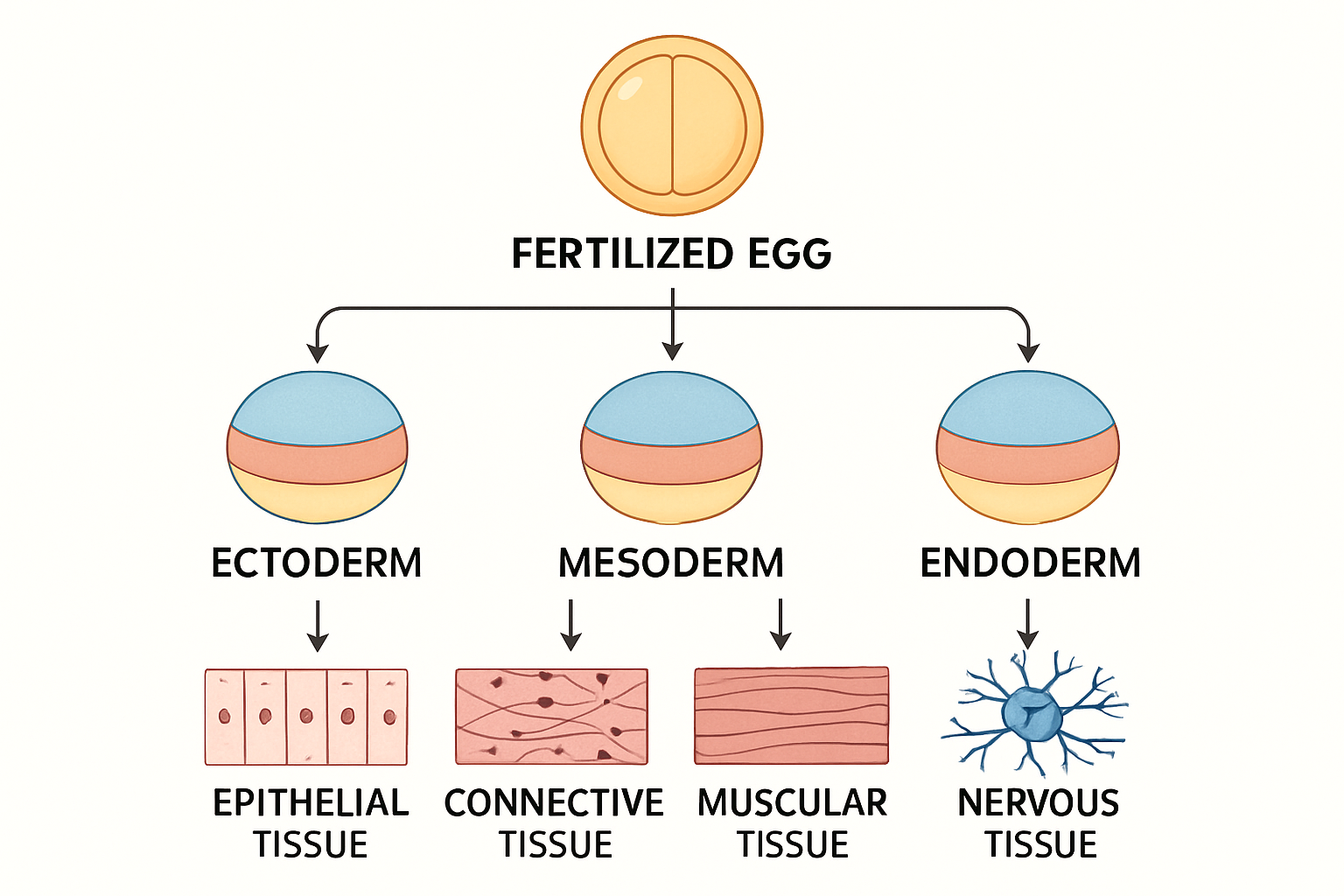
A fertilized egg divides to produce three primary germ cell layers. These layers differentiate to form the tissues of the body.Human body is composed of four basic types of tissue:
- Epithelial tissue
- Connective tissue
- Muscular tissue
- Nervous tissue
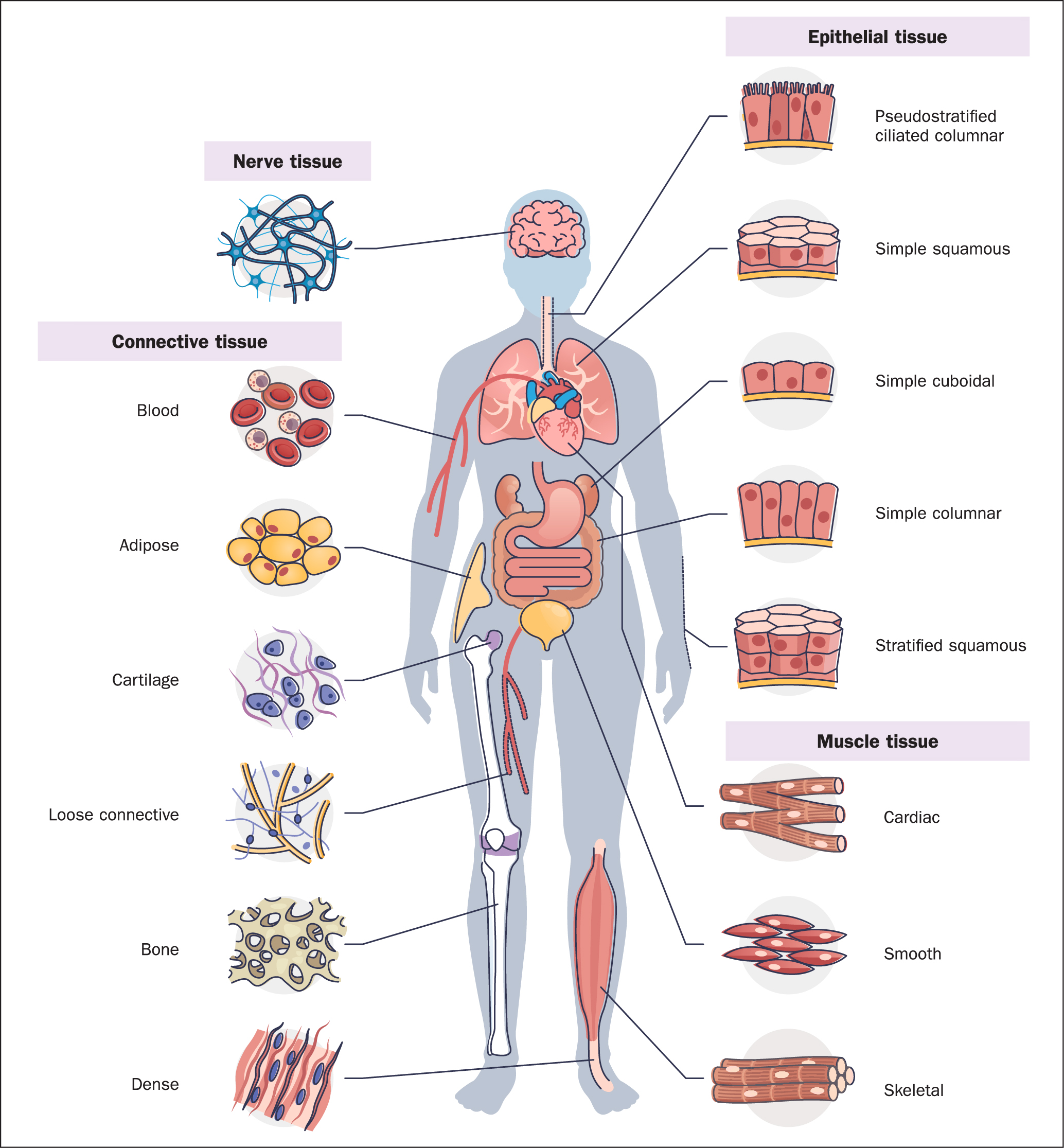
Epithelial Tissue
Epithelial cells cover or line all body surfaces, cavities, and tubes (covering epithelia). They also form the functional units of secretory glands (glandular epithelia).
General Characteristics
- Closely attached to each other forming a protective barrier
- One free (apical) surface open to outside or internal cavity
- One fixed (basal) surface attached to connective tissue
- Avascular but nourished by underlying connective tissue
- Innervated
- Highly regenerative (e.g., sunburn, skinned knee)
Functions
- Protection from radiation, desiccation, toxins, pathogens, trauma
- Regulation and exchange of chemicals
- Secretion of hormones, sweat, mucus, enzymes
- Sensation
- Absorption (gut lining)
- Filtration (kidney)
- Formation of secretory glands
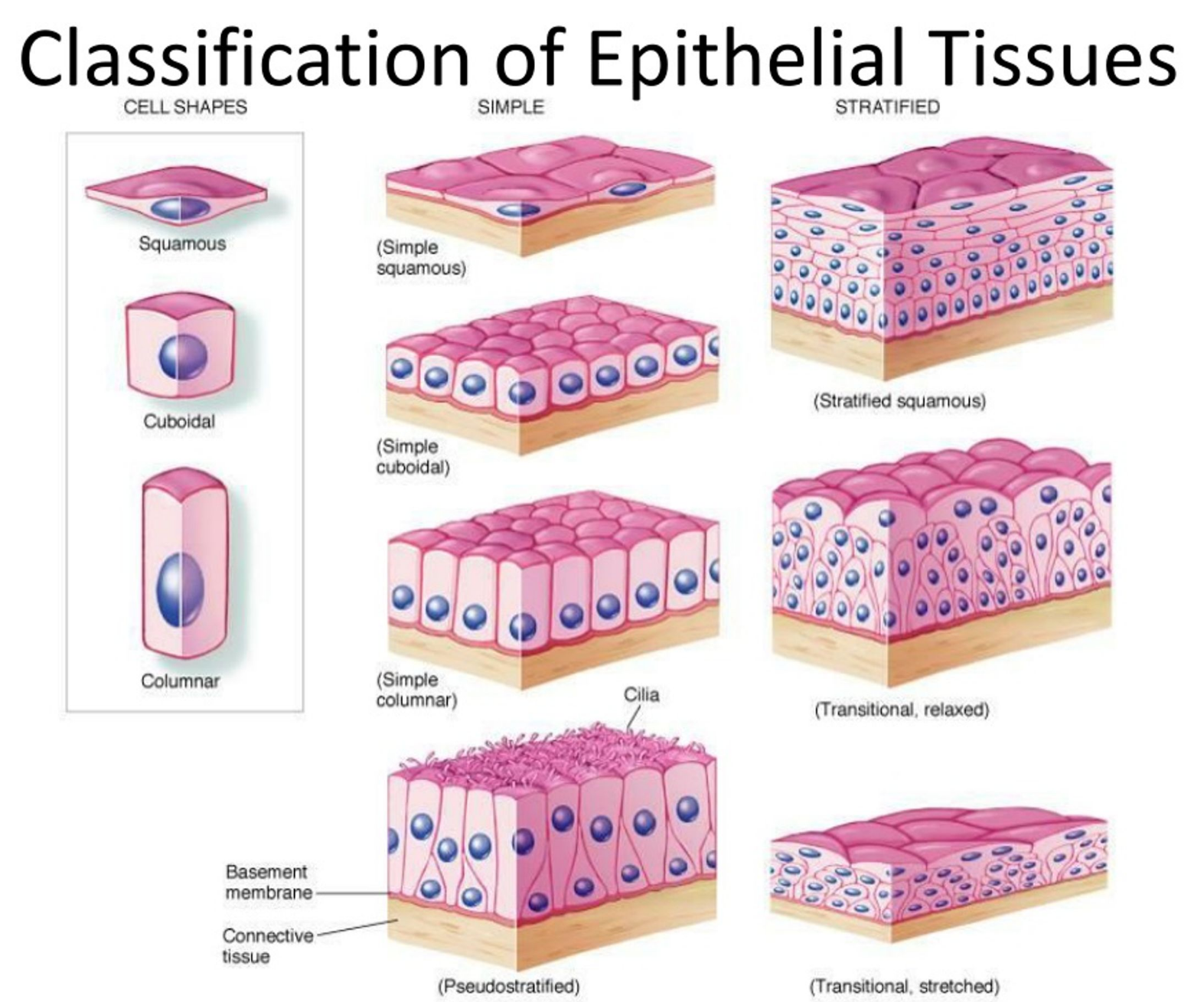
Classification of Epithelia
According to thickness:- Simple: One cell layer
- Stratified: More than one layer (named by apical cell shape)
- Squamous: Wider than tall
- Cuboidal: As tall as wide
- Columnar: Taller than wide
Types of Epithelial Tissue
-
Simple Squamous Epithelium
Description: Single layer of flattened cells with disc-shaped nuclei
Function: Passive transport of gases and fluids
Location: Alveoli, mesothelium, endothelium -
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
Description: Single layer of cubelike cells with spherical nuclei
Function: Secretion and absorption
Location: Kidney tubules, small gland ducts, ovary surface -
Simple Columnar Epithelium
Description: Single layer of tall cells with oval nuclei
Types: Ciliated and non-ciliated
Function: Absorption; secretion of mucus, enzymes
Location: Digestive tract, gall bladder -
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
Description: Multilayered; surface cells squamous, basal cells cuboidal
Function: Protection
Location: Oral cavity, cervix, anal canal -
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium
Description: Two layers of cube-like cells
Function: Protection
Location: Sweat, mammary, salivary gland ducts -
Stratified Columnar Epithelium
Description: Multilayered; superficial cells columnar
Function: Protection and secretion
Location: Male urethra (rare) -
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
Description: Single layer; all cells touch basement membrane, nuclei at different levels
Function: Mucus secretion and propulsion
Location: Trachea lining -
Transitional Epithelium
Description: Dome-shaped cells; shape changes
Function: Stretching and protection
Location: Bladder, part of urethra
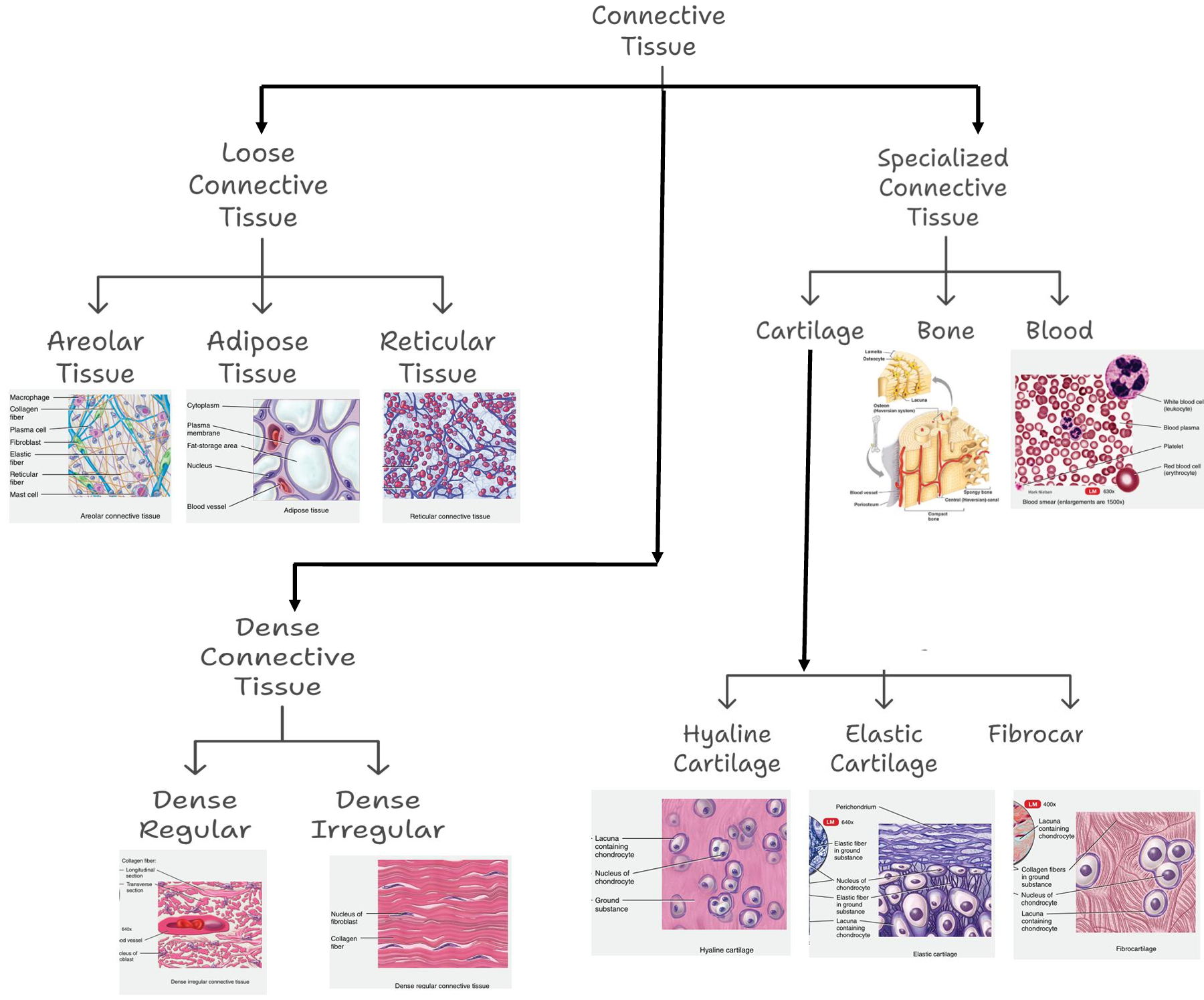
Connective Tissue
Connective tissues bind and support various parts of the body.
General Characteristics
- Abundant intercellular material, minimal cellular content
- Major component: Extracellular matrix (ECM)
- Contains cells, fibers, and ground substance
Functions
- Support and binding of tissues
- Fluid retention
- Defense against infection (macrophages, plasma cells, mast cells, WBCs)
- Fat storage
Types of Connective Tissue
-
Areolar Connective Tissue
Description: Gel-like matrix with all fiber types; includes fibroblasts, macrophages, mast cells, WBCs
Function: Phagocytosis, inflammation, fluid conveyance
Location: Under epithelia, around capillaries -
Adipose Tissue
Description: Sparse matrix; packed adipocytes with displaced nuclei
Function: Energy storage, insulation, organ protection
Location: Under skin, around kidneys/eyeballs, abdomen, breasts -
Reticular Tissue
Description: Network of reticular fibers in loose ground substance
Function: Internal skeleton for immune cells
Location: Lymph nodes, bone marrow -
Irregular Connective Tissue
Description: Irregular collagen fibers, some elastic fibers; fibroblasts
Function: Elasticity and support
Location: Dermis, digestive tract submucosa, joints -
Regular Connective Tissue
Description: Parallel collagen fibers, few elastic fibers; fibroblasts
Function: Muscle-to-bone and bone-to-bone attachment
Location: Tendons, ligaments -
Hyaline Cartilage
Description: Firm matrix; chondroblasts in lacunae
Function: Support, compression resistance
Location: Embryonic skeleton, long bone ends, nose cartilage -
Elastic Cartilage
Description: Similar to hyaline but with more elastic fibers
Function: Shape maintenance and flexibility
Location: External ear (pinna) -
Fibrocartilage
Description: Predominantly collagen fibers; less firm matrix
Function: Tensile strength, shock absorption
Location: Intervertebral discs, knee joints -
Bone
Description: Hard, calcified matrix with collagen; vascularized
Function: Support, protection, movement, mineral storage, blood formation
Location: Skeleton -
Blood
Description: Liquid matrix with red and white blood cells
Function: Transport of gases, nutrients, wastes
Location: Blood vessels