Experiment 14: Determination of Blood Pressure
Aim
To determine blood pressure.Requirements
- Stethoscope
- Sphygmomanometer
Reference
Practical handbook of Human Anatomy and Physiology by S.R. Kale. Nirali Prakashan, Eighth Edition, 2002, Page number: 36-38.Introduction
Arterial blood pressure is the force exerted by the blood on the wall of a blood vessel as the heart pumps (contracts) and relaxes. Systolic blood pressure is the degree of force when the heart is pumping (contracting). The diastolic blood pressure is the degree of force when the heart is relaxed.
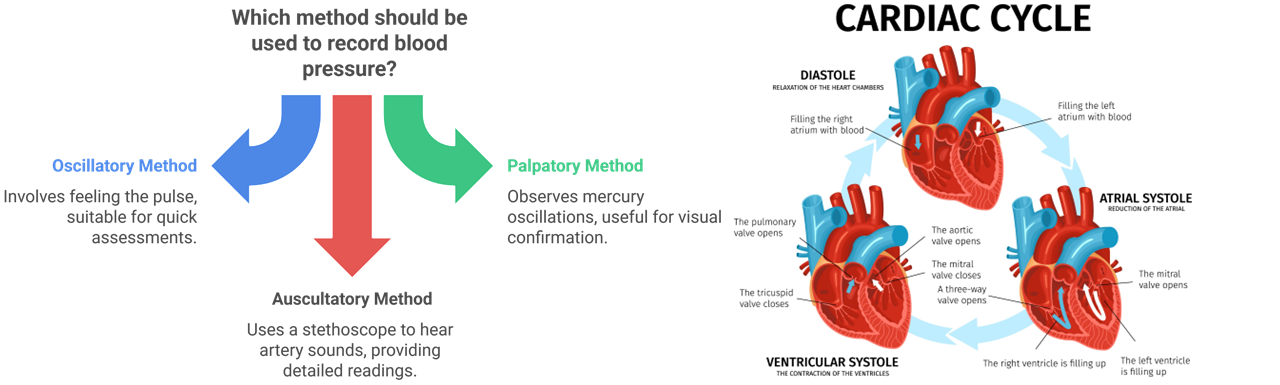
There are three methods for the recordation of the blood pressure:
- Oscillatory Method (Feeling the pulse)
- Palpatory Method (Observations of oscillations of the mercury level)
- Auscultatory Method (Hearing with the stethoscope the sound produced in the segment of the artery distal obstructions)
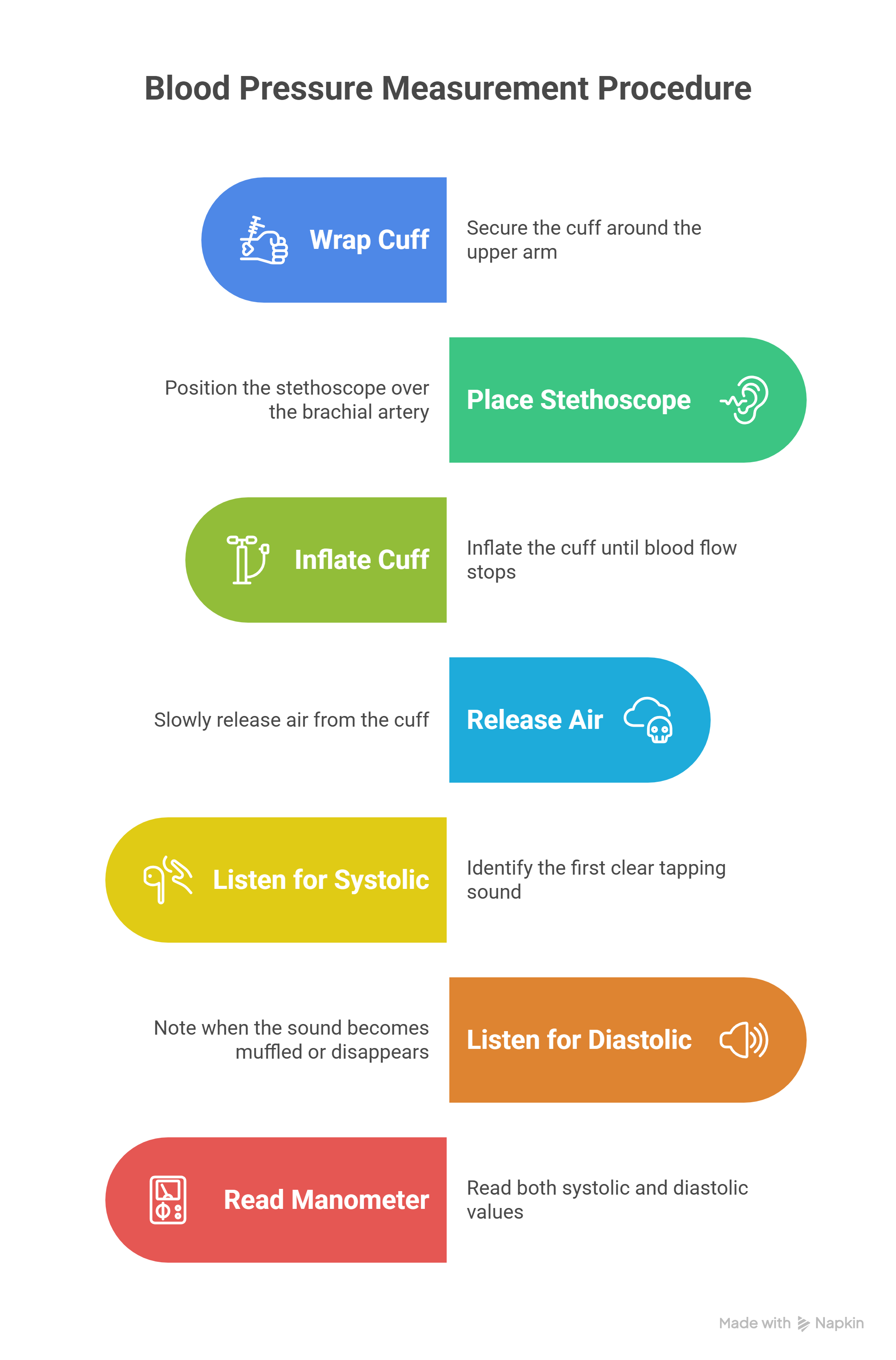
Procedure
- Wrap the cuff snugly around the upper arm, aligning the inflatable bag over the brachial artery.
- Place the stethoscope over the brachial artery in the antecubital space.
- Inflate the cuff until blood flow stops and no sound is heard.
- Slowly release air using the thumb valve.
- Listen for the first clear tapping sound—this indicates systolic pressure.
- Continue deflating; note when the sound becomes muffled or disappears—this indicates diastolic pressure.
- Read both values from the manometer.
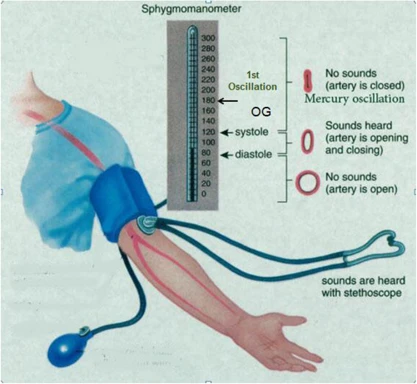
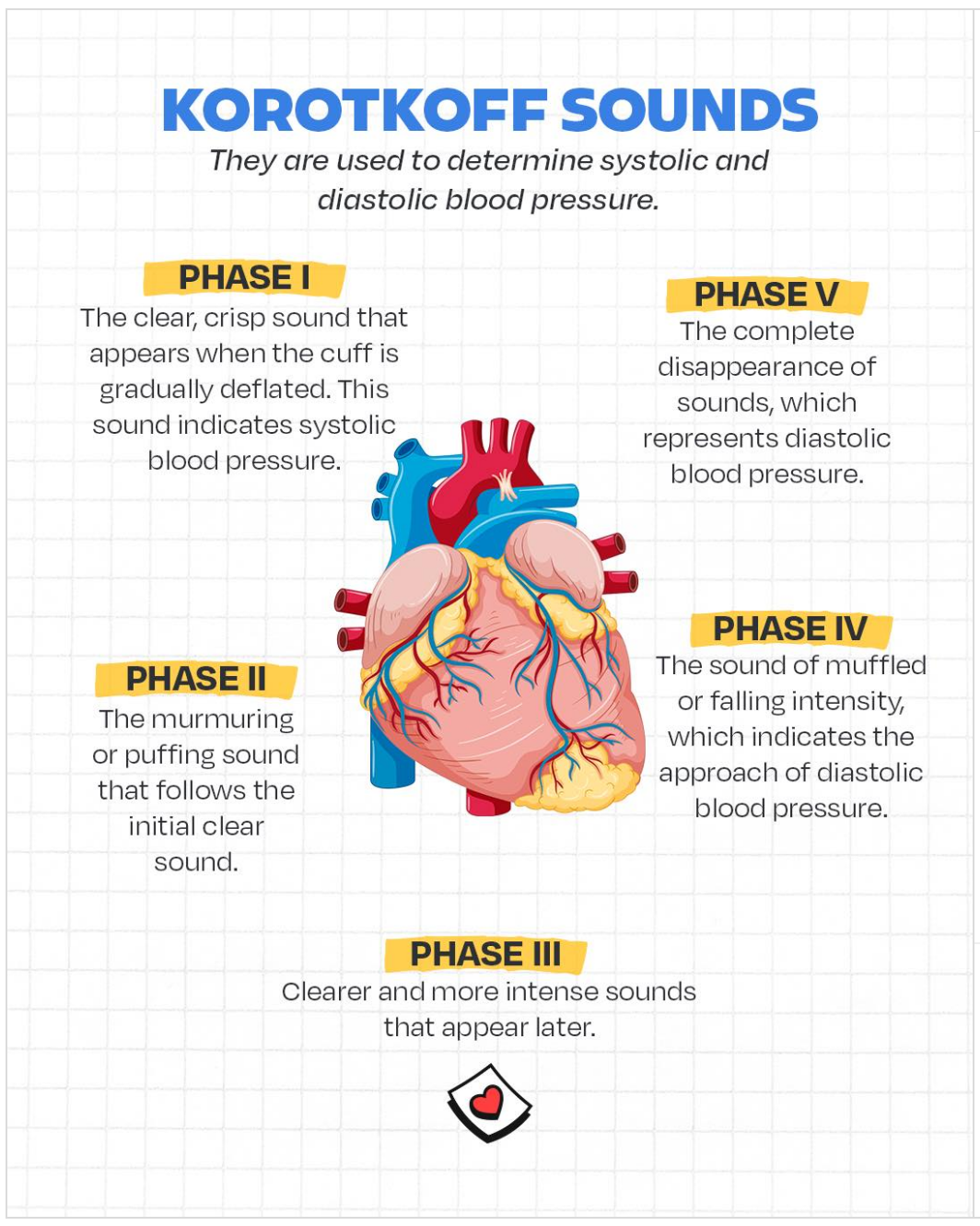
Phases of Blood Pressure Sounds
- Phase I: The sudden onset of a clear, tapping sound which becomes louder during the first 10 mm fall in pressure. Its first appearance indicates the systolic pressure.
- Phase II: The sound becomes softer, acquiring a murmured character, during the next 15 mm fall in pressure.
- Phase III: The murmur sound again is replaced by louder sound during the next 15 mm fall in pressure.
- Phase IV: The loud sound suddenly becomes softer and more muffled. This indicates diastolic pressure.
- Phase V: When the bag pressure is lowered further, all the sounds disappear.